Computer Science 15-111 (Sections A & B), Spring 2007
Class Notes: 02-Apr-2007
Logistics:
1.
Quiz 6 is Wednesday
Covers material through last Friday (including JCF, with today’s JCF redux)
2.
Reading on Trees:
a.
Wikipedia entries on:
i.
Trees
ii.
Binary Trees
iii.
Binary Search Trees
b.
Javanotes: Section 9.4
i.
9.4.0. Binary Trees
ii.
9.4.1. Binary Tree Traversals
iii.
9.4.2. Binary Sort Trees (we call them Binary Search
Trees)
iv.
9.4.3. Expression Trees
c.
Dr. Kesden’s class notes:
iii.
BST coding
Topics:
1.
JCF Redux (for Wednesday’s Quiz)
a.
A bit more on Maps
i.
Map
interface
1. Map:
An object that maps keys to values.
ii.
HashMap
1.
Map backed
by a hash table.
2.
Constant-time
get, put (assuming a good hash function)
3.
Unordered
(and order can change over time)
4.
Instances have two parameters affecting performance
a.
Initial Capacity
b.
Load Factor
i.
Rehash when (# of elements) > (capacity) x (load factor)
iii.
SortedMap
interface
1.
A map that
further guarantees that its iterator will traverse the map in ascending key
order
a.
Natural
order defined by Comparable; or
b.
By a
Comparator provided when the map is first created.
iv.
TreeMap
1.
SortedMap
backed by a (red-black) tree
a.
Self-balancing
binary search tree
b.
See Wikipedia entry on Red-Black
Trees
(Though you need
not know much about them, at least not yet, beyond what is mentioned here.)
2. O(logn)-time containsKey, get, put and remove
b.
Collections class
c.
Arrays
class
2.
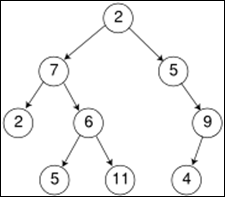
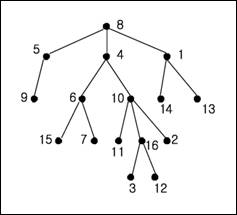
Tree Definitions
a.
Tree
b.
Nodes
i.
With and (more typically) without
Parent Pointers
c.
Values
d.
Duplicate Values
i.
Set (no duplicates)
ii.
Multiset (duplicates)
e.
Child Node
f.
Parent Node
g.
Root Node
h.
Sibling Node
i.
Ancestor Node
j.
Descendant Node
k.
Leaf Node
l.
Internal or Inner (Non-Leaf) Node
m.
Node Depth
n.
Tree Depth or Tree Height
o.
Subtree
p.
Proper Subtree
q.
Traversal or Walk
i.
Preorder Traversal
ii.
Inorder Traversal
iii.
Postorder Traversal
r.
Balanced Tree
s.
Full Tree
t.
Complete Tree
u.
Perfect Tree
w.
Binary Search Tree (BST)
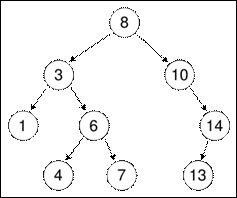
x.
Expression Tree

z.
Heap (A Complete, Partially-Ordered
Binary Tree)
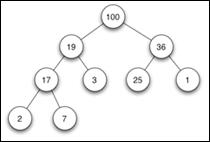
3.
BST Storage
a.
Linked Nodes
b.
Array
4.
BST Algorithms
a.
Searching
Iterate down
appropriate path.
b.
Insertion
Iterate down
appropriate path to leaf. Add new leaf.
c.
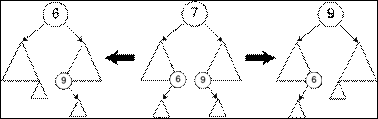
Deletion
i.
Deleting a leaf
Easy.
ii.
Deleting a node with one child
Delete it and
replace it with its child.
iii.
Deleting a node with two children
Replace node with
either:
1.
in-order successor; or
2.
in-order predecessor